Comprehensive Guide to Safe Pest Control Techniques
Introduction to Safe Pest Control
In the quest to maintain a comfortable and healthy living environment, pest control stands out as an essential aspect of home maintenance. Pests, ranging from insects to rodents, can pose significant threats to both property and health. However, the use of harsh chemicals in pest management has raised concerns about safety and environmental impact. This guide explores safe pest control techniques, offering homeowners effective strategies to manage unwanted invaders without compromising health or the environment.
Understanding Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic approach to pest control that emphasizes the use of multiple tactics to manage pest populations. This method prioritizes understanding the life cycle and behavior of pests to develop effective, sustainable control strategies. IPM combines cultural, biological, and physical control methods, reducing reliance on chemical pesticides. By focusing on long-term prevention and monitoring, IPM helps maintain a balance between pest control and environmental health.
Key components of IPM include:
- Monitoring and identifying pests accurately.
- Setting action thresholds to determine when management is needed.
- Implementing preventive measures to reduce pest attraction and entry.
- Using targeted control methods when necessary, prioritizing non-chemical options first.
IPM’s effectiveness lies in its adaptability; it can be tailored to specific environments and pest challenges, making it a widely recommended technique for safe pest control.
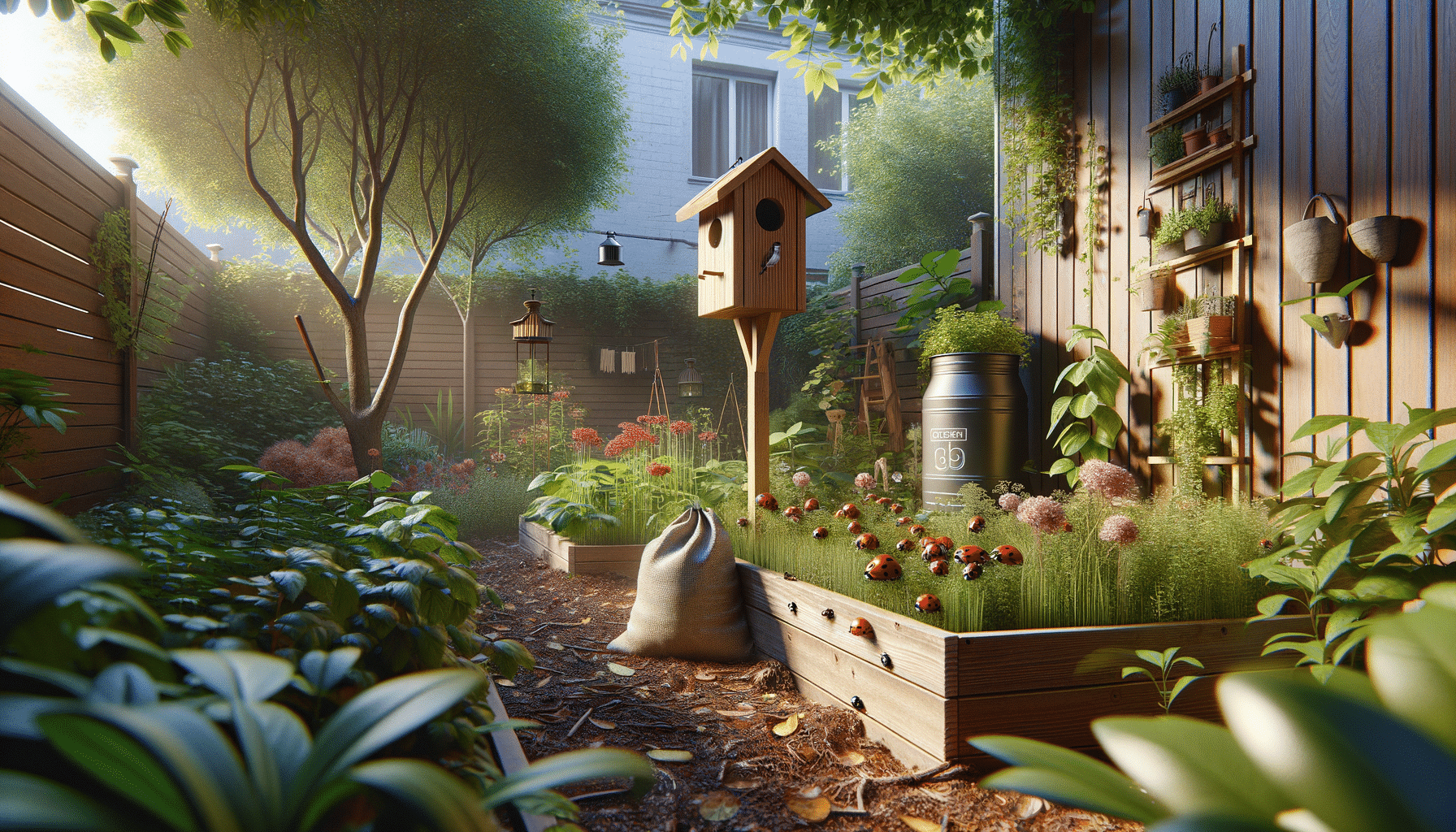
Biological Control Methods
Biological control involves using natural predators and parasites to manage pest populations. This method leverages the natural food chain, introducing or encouraging beneficial organisms that prey on or parasitize pests. For example, ladybugs are effective in controlling aphid populations, while certain types of nematodes can target soil-dwelling pests.
The advantages of biological control include its eco-friendliness and sustainability. Unlike chemical pesticides, biological agents do not leave harmful residues and are less likely to lead to pest resistance. However, successful implementation requires careful selection and management of biological agents to ensure they do not disrupt the existing ecosystem.
Examples of biological control agents include:
- Predatory insects like ladybugs and lacewings.
- Parasitic wasps that target specific pests.
- Microbial insecticides, such as Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), which target certain insect larvae.
By incorporating biological control methods into a pest management plan, homeowners can achieve effective pest control while supporting biodiversity and ecological balance.
Physical and Mechanical Control Techniques
Physical and mechanical pest control methods focus on using barriers, traps, and manual removal to prevent and manage pest infestations. These techniques are particularly useful for controlling large pests like rodents and birds, as well as small insects that can be physically intercepted.
Common physical control methods include:
- Sealing entry points to prevent pest access.
- Using traps such as glue boards or snap traps for rodents.
- Employing insect screens and nets to protect plants and crops.
- Utilizing heat or cold treatments to eliminate pests from stored products.
These methods are often combined with other control strategies to enhance effectiveness, offering a safe alternative to chemical interventions. While physical control can be labor-intensive, it provides a non-toxic solution that minimizes environmental impact.
Chemical Control with Caution
While non-chemical methods are preferred for safety and sustainability, there are situations where chemical control is necessary to manage severe pest infestations. In such cases, it is crucial to use chemical pesticides judiciously and responsibly to minimize risks to humans, pets, and the environment.
When considering chemical control, homeowners should:
- Select pesticides that are specifically labeled for the target pest.
- Follow label instructions meticulously to ensure safe application.
- Consider using less toxic options, such as botanical or natural-based pesticides.
- Apply pesticides in targeted areas to reduce exposure and environmental impact.
By integrating chemical control with other techniques, such as those outlined in IPM, homeowners can achieve effective pest management while upholding safety standards. It is always advisable to consult with pest control professionals to determine the most appropriate and safe solutions for specific pest challenges.
Conclusion: Achieving a Pest-Free Home Safely
Maintaining a pest-free home is essential for ensuring a safe and healthy living environment. By adopting safe pest control techniques, homeowners can effectively manage pest populations while minimizing harm to themselves and the environment. From integrated pest management to biological and physical methods, there are numerous strategies available that prioritize safety and sustainability.
Ultimately, the key to successful pest control lies in understanding the specific challenges posed by different pests and tailoring solutions accordingly. Whether through prevention, monitoring, or targeted interventions, safe pest control practices empower homeowners to protect their homes and health without compromising ecological integrity.